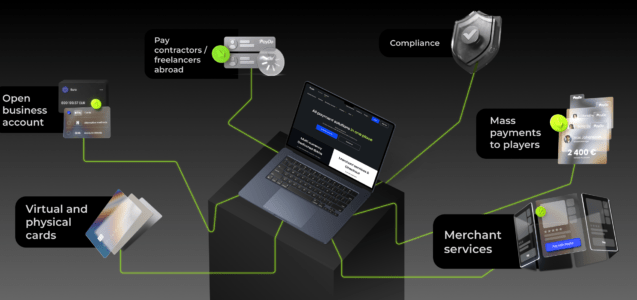
Embedded finance refers to integrating financial services into non-financial platforms, applications, or processes. It represents a paradigm shift in how financial products are offered and consumed. Rather than the end-user having to seek out and interact with a bank or financial institution directly, financial services are now embedded within the natural flow of the user’s digital journey.
The numbers only confirm the success of embedded financial services, as the market is likely to hold a revenue of $63.2 billion in 2023, with a potential value growth of $291.3 billion by 2033. Read more about this topic below as we explain all the necessary details about embedded finance and why it is crucial for businesses and consumers.
Embedded finance in simple terms
Think about playing a video game and finding a special tool inside the game to help you move ahead. Embedded finance is a bit like that but for everyday apps.
You’re on a shopping app looking at a cool jacket. When you’re about to buy it, the app says, “Hey, want to split this payment over three months?” This offer comes without you having to leave the app or visit a bank. That’s the magic of embedded finance!
Simply put, embedded finance sneaks banking tools into other apps, making it easy for us to handle money without jumping from a bank account from one place to another. It’s like having a mini-bank right inside your favourite apps!
Embedded finance examples
As many people in business believe – convenience is key. One of the latest advancements that exemplifies this principle is embedded finance. Rather than redirecting users to separate platforms or apps for financial tasks, embedded finance integrates these services directly into the user’s current activity, offering a boosted and hassle-free experience.
Specific examples
Let’s explore examples that showcase the power and versatility of embedded finance in our daily lives.
- Online Shopping. You’re buying a laptop on an e-commerce website, and right at the checkout, the site offers you a quick loan to spread the cost over a few months. You accept the loan without ever leaving the shopping site.
- Ride-hailing Apps. After you ride in a cab, the app lets you use its built-in wallet instead of paying with cash or a card. Some apps even offer car loans or insurance directly to their drivers.
- Social Media. While scrolling through a social media platform, you spot a friend’s post about a fundraising campaign. You click a button and instantly send money to support the cause, all within the same platform.
- Food Delivery Apps. While ordering food, the app allows you to “buy now, pay later.” You choose to pay in four small payments over the next month without needing a separate finance app.
- Health & Fitness Platforms. You decide to buy a premium fitness tracker. The app offers insurance for the device simultaneously, ensuring it’s protected from damage or loss.
- Event Booking Platforms. While purchasing tickets for a concert, the platform offers travel insurance or even a short-term loan for VIP tickets, making the entire booking process smoother.
- Home Rental Apps. When searching for a new apartment, the app provides an option to pay rent through a built-in payment system. Some may even offer rent insurance or financing options for larger security deposits.
These examples show how embedded finance reshapes our interactions with everyday apps, making life simpler and more interconnected.
The building blocks of embedded finance
Embedded financial solutions rapidly transform businesses’ operations, blending financial services effortlessly within non-financial applications. But what exactly forms the foundation of these solutions? We explore the core building blocks that enable this ongoing integration with non-financial business processes.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
- Role: APIs are the digital connectors that allow different software applications to talk to each other.
- In Embedded Finance: They enable the plug-and-play integration of financial services, like payments or lending, into other platforms, such as e-commerce websites or mobile apps.
Open Banking Platforms
- Role: These systems provide third-party developers access to financial data traditionally held by banks in a secure and standardized form.
- In Embedded Finance: Open banking platforms enable services like account aggregation, where users can view all their finances in one place, or payment initiation, bypassing traditional payment gateways.
White-label Solutions
- Role: These are ready-made, customizable financial products that companies can brand as their own.
- In Embedded Finance: Businesses can adopt and integrate services like white-label digital wallets or lending platforms without building them from scratch.
Data Analytics & AI
- Role: These tools process vast amounts of data to derive insights and predictions.
- In Embedded Finance: They help personalise financial offers, risk assessment for lending, fraud detection, and enhancing overall user experience.
Regtech Solutions
- Role: Regtech (or Regulatory Technology) helps companies navigate and comply with financial regulations.
- In Embedded Finance: Ensures that integrated financial services adhere to local and international regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance for businesses.
Digital Identity Verification
- Role: This ensures that the user accessing the service is genuinely who they claim to be.
- In Embedded Finance: Critical for Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, enabling secure onboarding and reducing fraud.
Payment Processors
- Role: They handle transactions, ensuring funds move securely between parties.
- In Embedded Finance: Allows businesses to accept payments or facilitate payouts within their platforms.
Cloud Infrastructure
- Role: Provides the digital architecture and resources to host, run, and scale applications.
- In Embedded Finance: Ensures that financial integrations are scalable and always available.
These building blocks serve as the foundational elements for embedded financial solutions. Combined thoughtfully, they allow businesses across sectors to offer sophisticated financial services smoothly and user-friendly, expanding their value proposition and fostering deeper customer relationships.

Why embedded finance is more than just a buzzword
Embedded payments have recently become a trending term in the fintech and broader tech industry. But are they merely a fleeting buzzword, or do they represent a genuine shift in how businesses handle transactions? We dive into the substantive reasons behind the rise and relevance of embedded payments.
Integrated Customer Experience
Embedded payments allow payment functionalities to be integrated directly into software applications or platforms. Users don’t need to leave an app or website to complete a payment. This ongoing experience increases conversion rates and boosts user satisfaction.
Operational Efficiency
By incorporating payments directly into their platforms, businesses can boost operations. It reduces the need for manual payment processing, minimizes errors, and speeds up transaction times, leading to cost savings and increased efficiency for software companies.
Data-Driven Insights
With payments being part of the platform, businesses can gather rich transaction data. This data helps better understand customer behaviours, tailor offerings, optimise pricing strategies, and predict market trends.
Enhanced Security
Modern embedded banking and payment solutions have advanced security features like tokenization and end-to-end encryption. They reduce the risk of data breaches and fraud, ensuring that businesses and their customers are protected.
Global Reach
Embedded payment platforms often support multicurrency transactions and a variety of payment methods. Businesses can cater to a global audience and meet the diverse payment preferences of different regions.
Embedded payments represent a strategic move towards smarter, faster, and more customer-centric transaction methods. As the digital landscape becomes more interconnected, the significance of embedded payments is bound to grow, making them a cornerstone of modern business operations.
The five strategic advantages of adopting embedded finance
Beyond the buzz, adopting embedded finance offers organizations distinct strategic advantages. Here are five of the most compelling benefits offered by embedded finance:
1. Deepening customer engagement
This increases user stickiness and fosters loyalty. Customers might stay longer on a platform if they can, for instance, shop, pay, and finance purchases all in one place. It also enhances the user experience by eliminating the need to juggle multiple apps or platforms.
2. Diversifying revenue streams
Companies can earn from transaction fees, interest, premiums, or even data-driven insights. For instance, an e-commerce platform embedding lending options can benefit from interest or a share of the loan origination fees, providing a new income source beyond just sales.
3. Personalized offerings
Businesses can offer tailored financial products based on user behaviour, preferences, and history. This level of personalization can lead to higher conversion rates, as offers are more aligned with individual user needs.
4. Accelerating market expansion
By integrating and embedding financial services and solutions, companies can appeal to a broader audience, facilitating quicker market penetration. For example, a gig economy platform offering embedded insurance or payment solutions might attract more freelancers or service providers.
5. Staying ahead in the competitive landscape
Offering embedded financial services can be a differentiator, setting a platform apart from competitors. By continuously innovating and enhancing embedding financial services offerings, businesses can position themselves as leaders in their core industry and the broader digital ecosystem.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
Embedded finance has revolutionized how businesses integrate financial services into their platforms, enhancing user experiences and creating new revenue avenues non financial companies. Yet, like all innovations, it’s not without its challenges.
- User Experience (UX). One of the first stumbling blocks businesses might face is delivering a poor user experience. Users can become frustrated when financial services feel clunky or don’t mesh well with the primary platform. To counteract this, businesses should emphasize UX design from the outset, collaborate with expert designers, and continually test and refine based on user feedback.
- Regulatory Non-Compliance. Another significant concern is regulatory non-compliance. The world of finance is riddled with regulations, and overlooking them can lead to severe penalties. Staying updated on local and international regulations is essential. It might also be beneficial to partner with fintech providers who are well-versed in these regulations or to seek frequent legal consultations to ensure full compliance.
- Security. Security is paramount in any financial transaction. Given the sensitive nature of financial data, any security lapse can lead to a loss of trust and potential legal complications. Businesses must invest heavily in security measures, ensuring that in-house and third-party systems maintain the highest standards.
- Mismatched Financial Products. Not every financial service will fit smoothly into every platform. Businesses might sometimes integrate financial products that their users don’t find valuable. Hence, it’s crucial to undertake rigorous market research and user segmentation to ensure the offerings resonate with the target audience.
While embedded finance offers significant advantages, it’s essential to approach its integration with foresight and diligence. By being proactive, staying informed, and prioritizing user needs, businesses can maximize the benefits of embedded finance solutions while minimizing potential pitfalls.
The embedded finance future
Embedded finance is more than just a trend; it’s a transformative movement reshaping the traditional boundaries of the traditional financial institutions and technological sectors. From our perspective, we see a future where it is not just an additive feature but a fundamental pillar of our digital experiences.
Integrated life experiences
In the future, embedded finance will smoothly blend our daily activities with financial transactions. Imagine planning a vacation using a travel app which lets you book flights and hotels, offers tailored travel insurance, provides foreign currency exchanges, and even suggests personalized saving plans or micro-loans for your trip – all within the same platform. This kind of integrated experience and financial product will become the norm rather than the exception.
Democratization of financial services
The digital transformation of finance has led to the rise of embedded finance products, providing a smooth gateway for people to access financial services. This paradigm shift has been revolutionary, especially for regions where traditional banking infrastructures are scarce or absent.
With the advent of mobile applications incorporating embedded finance, services such as banking, lending, insurance, and even wealth management are now available at one’s fingertips. This democratises access and plays a pivotal role in fostering financial inclusion, reducing the gap between the banked and unbanked populations.
Hyper-personalization
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics are shaping the future of embedded finance, making hyper-personalization a reality. Unlike the generic financial offerings of yesteryears, embedded finance platforms can now analyze user behaviours, preferences, and detailed financial histories in real time.
As a result, users can receive recommendations for investment strategies tailored to their risk appetite, spending tips aligned with their consumption patterns, and lending options suited to their credit profile. This shift towards tailored financial guidance increases user engagement and promotes responsible financial decision-making.
Regulatory evolution
The surge in embedded finance’s popularity isn’t without its regulatory challenges. The need for clear and comprehensive regulatory frameworks becomes paramount as the ecosystem becomes more intertwined with everyday services. Anticipating this evolution, regulators might introduce more defined and potentially stricter guidelines to safeguard consumer interests.
Companies operating within this domain, especially those involved in embedded lending, must display agility. The dual challenge of navigating the evolving regulatory landscape while upholding transparency and security standards will become a focal point of their operational strategies.
New business models
Embedded finance is not just a technological advancement; it’s a catalyst for business innovation. With its integration, companies are presented with opportunities to devise new monetization strategies. Businesses can enhance their value propositions by leveraging embedded finance providers and incorporating financial services into their platforms.
Revenue streams might diversify, with subscription models, transaction-based fees, or even the sale of data-driven insights becoming more prevalent. As financial services become integral to platforms across industries, the boundary between finance and other sectors will blur, leading to unprecedented collaborations and business models.
Challenges in cybersecurity
The integration and interdependence of embedded finance also introduce a complex web of cybersecurity challenges. As platforms become increasingly interconnected, they become potential hotspots for vulnerabilities. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures, including end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and real-time threat detection, becomes essential.
Continuous monitoring and prompt incident response mechanisms will maintain user trust. As the stakes are high, companies must prioritize cybersecurity as a technical requirement and a cornerstone of their brand’s promise to users.
Embedded finance in the future means that handling money will blend smoothly into our daily online activities. Instead of being separate, money matters become a quiet part of our online activities. Businesses and people will benefit from this easy-to-use setup as different areas come together.
Final recap
Embedded finance represents the fusion of financial services into non-financial platforms and applications. It’s more than just a technological innovation; it’s a transformative shift in how we interact with financial products daily. For businesses, it opens avenues for enhanced user engagement, diversified revenue streams, and a deeper understanding of consumer behaviours.
For individuals, it offers convenience, tailored experiences, and greater accessibility. In the modern world, where agility and integration are paramount, embedded finance is pivotal in bridging the gap between traditional financial services and the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Stay informed with us to get more!