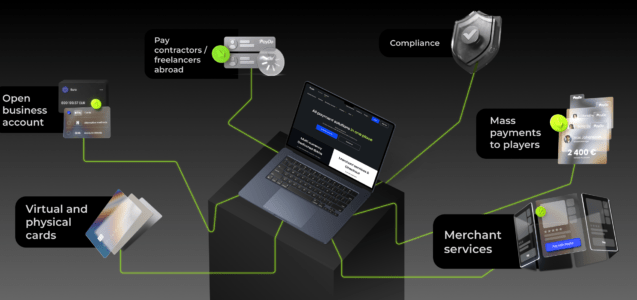
Globalization and digital services have changed how companies do business, making e-commerce a key tool for buying, selling, and providing services online. The market is expected to reach $6.4 trillion by 2024. Such massive growth shows how important online transactions have become for businesses. A small business in the EU can now easily sell products globally through an online platform, reaching millions of people worldwide.
In this piece, let’s find out the secret of e-commerce. What makes it so popular and whether there are any hidden gems. Stay tuned.
What Makes E-commerce Work So Good?
The foundation of marketplace success — the Internet. There are currently 5.45 billion Internet users and potential e-commerce customers.
The second major thing driving e-commerce success is the mobile phone. There are more than 15 billion mobile phones in the world. Almost twice the global population.
The Internet and mobile devices created the perfect conditions for e-commerce to arise. E-commerce has changed the economy over the past 40 years. It has risen due to advances in technology since the 1980s.
Apart from the Internet and mobile technology, the more current e-commerce drivers are the following:
- Payment Gateway Technology
- Data and Analytics
- Social Networking

1. Payment Gateway Technology
This is the main tool for e-commerce. With it, buyers and sellers make transactions via different payment methods. These can be debit, credit, transfers, electronic wallets, and so on. Thanks to e-commerce, the world is slowly moving to digital currency.
Imagine you’re shopping online and want to buy something. You can pay using your credit card, debit card, or even an electronic wallet like PayDo. E-commerce makes it easy to pay in different ways, and over time, more people are using digital money instead of cash.
2. Data and Analytics
Every day, Internet users generate about 402,000,000,000 gigabytes of data. Most of this raw data is hard to use. However, some of it contains invaluable insights that help understand customer needs.
E-commerce businesses use data and analytics to make decisions. Organizations search, group, and analyze customer data points. The more data grows, the more we need to study users of services and buyers.
For example, merchants can calculate digital ROI online by accessing real-time knowledge. E-commerce users use analytics to determine a customer’s required order quantity and conversion rate.
3. Social Networking
For a long time, it has been a place for communication and a platform for advertising. Blogs, apps, mailing lists, banners, and posters help all forms of e-commerce grow by bringing people together and spreading information among them.
Social networks direct and remind the client about the service. This helps maintain their interest. With the help of social media, building a brand and getting an audience grouped by interests are easy.
Different E-commerce Types
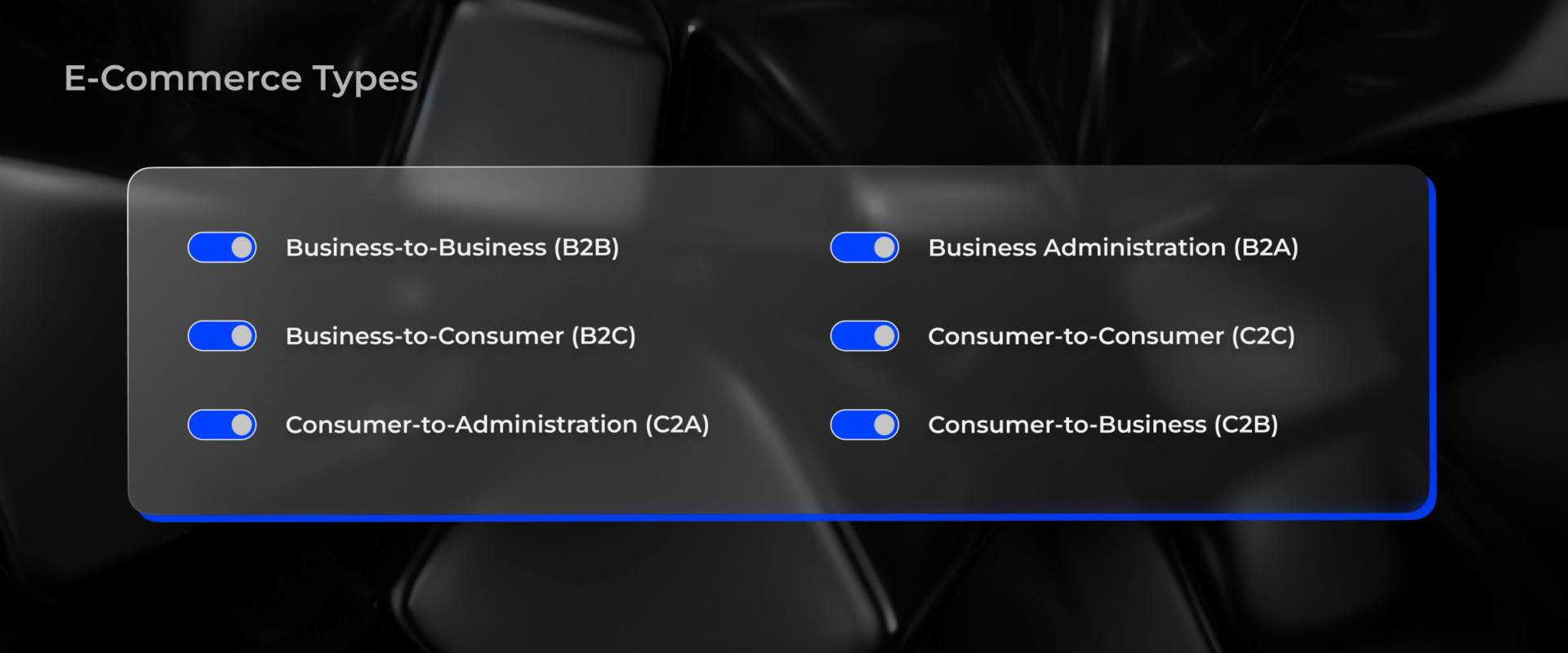
Of course, two main types of e-commerce are most frequently mentioned everywhere. Still, it is better to consider more types to understand the difference better.
- Business-to-Business (B2B). All products and services happen between two business entities – firms, companies, and enterprises. Example: Wholesale companies in the field of industry or manufacturers of goods and services for business.
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C). Companies directly interact with consumers. Example: When you buy a product from Amazon or order food through an app like Uber Eats.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C). The sale and purchase of goods and services between consumers. Typically, buying and selling is done by a third party that provides a platform for online transactions.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B). This is a reverse e-commerce type that is the opposite of conventional commerce. Often C2B can be found in companies that are engaged in crowdsourcing. Individuals can sell their services and products to highly specialized companies. For example, a company needs a logo – they order several options choose one, and buy. In this business segment, there are exchanges of photos and other media elements.
- Business Administration (B2A). Any online transaction between the government and companies. These are well-known processes: taxation, health care operations, social assistance, business reports, legal documentation, etc.
- Consumer to Administration (C2A). This business segment means buying between the government and the individual. First, this means education – online learning, information dissemination, and the like. This includes taxes, payments, and filing tax returns.
Do not forget about the health sector: payment for services in the field of medicine and obtaining information about diseases. Let’s consider the pros and cons of e-commerce so businesses can understand this issue better.
Pros of E-commerce

It can be assumed that the main thing for the consumer in e-commerce is that he saves time and energy because he can order from anywhere and receive it anywhere on the globe.
The benefits of e-commerce include:
- Low rates for people entering the stock exchange.
- Consumers can make purchases regardless of the time of day and without contacting the seller’s company.
- Saving time, the buyer can place an order in a few clicks and pay for it with delivery.
- Access to a large amount of information allows you to study the market and make the right choice.
- Being at home, the buyer makes purchases of goods and services in complete comfort, which improves the quality of shopping.
- It is easy to change the seller company if the perfect purchase is not good enough.
- There is a high probability of finding the right product in stock, as the user has a wider selection on the Internet.
- The ability to view and comment on a product or service provides an opportunity to obtain independent information before making a final purchase.
Cons of E-commerce

E-commerce is no exception, and it is possible to face problems with it. Most often, sellers and buyers use the Internet as a medium for doing business. The following are possible issues you may encounter:
- Private and public companies grow separately from e-commerce, but their collaboration with digital technologies is necessary to accelerate the process and increase the potential scale of growth.
- There are cases when no system would protect and ensure reliability, fulfill special requirements, and support communication protocols. If the website where the buyer made the purchase is hacked, customers will lose their money and the company’s income.
- All sorts of banks and financial organizations are not actively taken to support these types of e-commerce businesses. Otherwise, it would make it possible to expand and popularize e-commerce, prevent possible losses, and reduce theft and fraud with credit cards. But that would put the banks at risk.
Surprisingly, in some countries, purchases are made through bargaining to this day, so this culture can create certain problems in e-commerce.
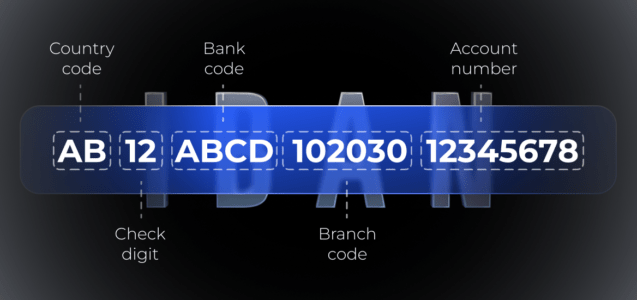
Maintaining confidence in the calculations on the Internet is difficult and very important. The issuance of electronic invoices is the basic documentation of laws and regulations that ensure the legitimacy of online transactions.
Conclusion
E-commerce has changed how businesses operate. It allows companies to reach a global audience. And it also lets consumers shop from anywhere, at their convenience.
As the industry grows, knowing its basics and challenges is vital. With the right tools, businesses can thrive in today’s digital economy. E-commerce can help do it. If you are searching for a reliable payment service provider, learn more about PayDo. Managing your business and personal accounts online and controlling your funds is easy.